Groundwater contamination by antibiotics: Review of sources, environmental factors and mobility
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55996/dekamuagropec.v6i2.331Abstract
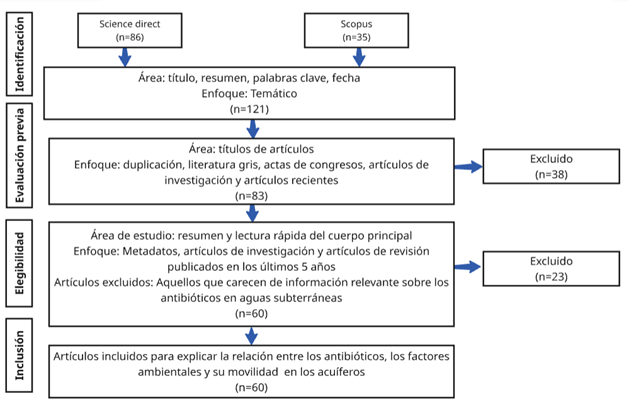
Groundwater contamination by antibiotics poses an emerging risk to health and ecosystems due to their increasing use and persistence. The objective of this review was to identify the main sources, environmental factors, and mechanisms that determine the presence of these compounds in aquifers. The methodology was based on PRISMA principles, with a systematic search of the ScienceDirect and Scopus databases, resulting in the analysis of 60 articles published between 2015 and 2024. It was determined that wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs), together with agricultural, livestock, industrial, and hospital activities, are the predominant sources of input. Sulfonamides, tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones, and macrolides have been detected in aquifers in Asia, Europe, and America, in some cases exceeding ecological risk values. Their mobility and persistence depend on pH conditions, soil texture, dissolved organic matter (DOM), temperature and redox conditions, which control the processes of adsorption, leaching and degradation. In conclusion, this review shows that the presence of antibiotics in aquifers is explained by the complex interaction between anthropogenic sources and environmental factors.
Downloads
References
Alzola-Andrés, M., Domingo-Echaburu, S., Segura, Y., Valcárcel, Y., Orive, G., & Lertxundi, U. (2023). Pharmaceuticals in hospital wastewaters: an analysis of the UBA’s pharmaceutical database. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(44), 99345–99361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29214-0
Anh, H. Q., Le, T. P. Q., Da Le, N., Lu, X. X., Duong, T. T., Garnier, J., Rochelle-Newall, E., Zhang, S., Oh, N.-H., Oeurng, C., Ekkawatpanit, C., Nguyen, T. D., Nguyen, Q. T., Nguyen, T. D., Nguyen, T. N., Tran, T. L., Kunisue, T., Tanoue, R., Takahashi, S., … Nguyen, T. A. H. (2021). Antibiotics in surface water of East and Southeast Asian countries: A focused review on contamination status, pollution sources, potential risks, and future perspectives. Science of The Total Environment, 764, 142865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142865
Astaíza Martínez, J. M., Benavides Melo, C. J., López Córdoba, M. J., & Portilla Ortiz, J. P. (2014). Diagnóstico de los principales antibióticos recomendados para pollo de engorde (broiler) por los centros agropecuarios del municipio de Pasto, Nariño, Colombia. Revista de Medicina Veterinaria, 27, 99. https://doi.org/10.19052/mv.3027
Bohrer, R. E. G., Carissimi, E., Lopez, D. A. R., Wolff, D. B., Silva, D. M. da, & Prestes, O. D. (2019). Compostagem de efluente suíno no tratamento de resíduos de fármacos veterinários. Semina: Ciências Agrárias, 40(6), 2813. https://doi.org/10.5433/1679-0359.2019v40n6p2813
Booth, A., Aga, D. S., & Wester, A. L. (2020). Retrospective analysis of the global antibiotic residues that exceed the predicted no effect concentration for antimicrobial resistance in various environmental matrices. Environment International, 141, 105796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105796
Bouzid, J., Jaouhar, S., Zaid, A., Bouhlou, L., & Chahlaoui, A. (2021). Evaluation of the bacteriological and physicochemical risk of hospital effluents: case of the Mohamed V hospital in Meknes. E3S Web of Conferences, 319, 01105. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202131901105
Cavaco, L. M., Abatih, E., Aarestrup, F. M., & Guardabassi, L. (2008). Selection and Persistence of CTX-M-Producing Escherichia coli in the Intestinal Flora of Pigs Treated with Amoxicillin, Ceftiofur, or Cefquinome. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 52(10), 3612–3616. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00354-08
Charuaud, L., Jarde, E., Jaffrezic, A., Thomas, M.-F., & Le Bot, B. (2019). Veterinary pharmaceutical residues from natural water to tap water: Sales, occurrence and fate. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 361, 169–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.08.075
Chen, L., Lang, H., Liu, F., Jin, S., & Yan, T. (2018). Presence of Antibiotics in Shallow Groundwater in the Northern and Southwestern Regions of China. Groundwater, 56(3), 451–457. https://doi.org/10.1111/gwat.12596
Choi, T.-M., Chiu, C.-H., & Chan, H.-K. (2016). Risk management of logistics systems. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 90, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tre.2016.03.007
Couto, C. F., Lange, L. C., & Amaral, M. C. S. (2019). Occurrence, fate and removal of pharmaceutically active compounds (PhACs) in water and wastewater treatment plants—A review. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 32, 100927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.100927
De Mastro, F., Cacace, C., Traversa, A., Pallara, M., Cocozza, C., Mottola, F., & Brunetti, G. (2022). Influence of chemical and mineralogical soil properties on the adsorption of sulfamethoxazole and diclofenac in Mediterranean soils. Chemical and Biological Technologies in Agriculture, 9(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40538-022-00300-8
Espíndola, J. C., & Vilar, V. J. P. (2020). Innovative light-driven chemical/catalytic reactors towards contaminants of emerging concern mitigation: A review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 394, 124865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124865
European Medicines Agency. (2018). Sales of veterinary antimicrobial agents in 30 European countries in 2016- Trens from 2010 to 2016- Eight ESVAC report. European Medicines Agency, 176. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/report/sales-veterinary-antimicrobial-agents-30-european-countries-2016-trends-2010-2016-eighth-esvac_en.pdf%0Ahttp://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Report/2016/10/WC500214217.pdf
Fang, L., Zhou, Y., Huang, Z., Yang, G., Li, T., Song, C., & Chen, J. (2021). Dynamic Elimination of Enrofloxacin Under Varying Temperature and pH in Aquaculture Water: An Orthogonal Study. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 106(5), 866–872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03199-3
FAO. (2024). FAO AQUASTAT Dissemination System. In AQUASTAT Website. https://data.apps.fao.org/aquastat/?lang=en
Fenollar Penadés, A. (2020). Estudio de la transmisión de resistencias a antibióticos mediante métodos moleculares en el sector avícola y su implicación para la salud pública [Universitat Politècnica de València]. https://doi.org/10.4995/Thesis/10251/149399
Fu, C., Xu, B., Chen, H., Zhao, X., Li, G., Zheng, Y., Qiu, W., Zheng, C., Duan, L., & Wang, W. (2022). Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in groundwater, surface water, and sediment in Xiong’an New Area, China, and their relationship with antibiotic resistance genes. Science of The Total Environment, 807, 151011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151011
Garcia, J. F., Diez, M. J., Sahagun, A. M., Diez, R., Sierra, M., Garcia, J. J., López, C., & Fernandez, M. N. (2022). Availability of Antibiotics for Veterinary Use on the Internet: A Cross-Sectional Study. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2021.798850
Geissen, V., Mol, H., Klumpp, E., Umlauf, G., Nadal, M., van der Ploeg, M., van de Zee, S. E. A. T. M., & Ritsema, C. J. (2015). Emerging pollutants in the environment: A challenge for water resource management. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 3(1), 57–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2015.03.002
González-Pérez, D. M., Pérez, J. I., & Gómez, M. A. (2017). Behaviour of the main nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in a membrane bioreactor treating urban wastewater at high hydraulic- and sludge-retention time. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 336, 128–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.04.059
Gothwal, R., & Shashidhar, T. (2015). Antibiotic Pollution in the Environment: A Review. CLEAN – Soil, Air, Water, 43(4), 479–489. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201300989
Gros, M., Catalán, N., Mas-Pla, J., Čelić, M., Petrović, M., & Farré, M. J. (2021). Groundwater antibiotic pollution and its relationship with dissolved organic matter: Identification and environmental implications. Environmental Pollution, 289, 117927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117927
Gude, V. G., & Maganti, A. (2021). Desalination of deep groundwater for freshwater supplies. In Global Groundwater (pp. 577–583). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-818172-0.00042-6
Hara, K., Kuroda, M., Yabar, H., Kimura, M., & Uwasu, M. (2016). Historical development of wastewater and sewage sludge treatment technologies in Japan – An analysis of patent data from the past 50 years. Environmental Development, 19, 59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envdev.2016.05.001
Harrower, J., McNaughtan, M., Hunter, C., Hough, R., Zhang, Z., & Helwig, K. (2021). Chemical Fate and Partitioning Behavior of Antibiotics in the Aquatic Environment—A Review. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 40(12), 3275–3298. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5191
He, L.-Y., He, L.-K., Liu, Y.-S., Zhang, M., Zhao, J.-L., Zhang, Q.-Q., & Ying, G.-G. (2019). Microbial diversity and antibiotic resistome in swine farm environments. Science of The Total Environment, 685, 197–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.369
Hubeny, J., Harnisz, M., Korzeniewska, E., Buta, M., Zieliński, W., Rolbiecki, D., Giebułtowicz, J., Nałęcz-Jawecki, G., & Płaza, G. (2021). Industrialization as a source of heavy metals and antibiotics which can enhance the antibiotic resistance in wastewater, sewage sludge and river water. PLOS ONE, 16(6), e0252691. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0252691
Khurana, P., Pulicharla, R., & Kaur Brar, S. (2021). Antibiotic-metal complexes in wastewaters: fate and treatment trajectory. Environment International, 157, 106863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2021.106863
Kivits, T., Broers, H. P., Beeltje, H., van Vliet, M., & Griffioen, J. (2018). Presence and fate of veterinary antibiotics in age-dated groundwater in areas with intensive livestock farming. Environmental Pollution, 241, 988–998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.05.085
Kulik, K., Lenart-Boroń, A., & Wyrzykowska, K. (2023). Impact of Antibiotic Pollution on the Bacterial Population within Surface Water with Special Focus on Mountain Rivers. Water, 15(5), 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15050975
Lin, Y.-C., Lai, W. W.-P., Tung, H., & Lin, A. Y.-C. (2015). Occurrence of pharmaceuticals, hormones, and perfluorinated compounds in groundwater in Taiwan. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(5), 256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4497-3
Liu, X., Zhang, G., Liu, Y., Lu, S., Qin, P., Guo, X., Bi, B., Wang, L., Xi, B., Wu, F., Wang, W., & Zhang, T. (2019). Occurrence and fate of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in typical urban water of Beijing, China. Environmental Pollution, 246, 163–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.12.005
Liu, Z., Lu, Y., Wang, P., Wang, T., Liu, S., Johnson, A. C., Sweetman, A. J., & Baninla, Y. (2017). Pollution pathways and release estimation of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in central and eastern China. Science of The Total Environment, 580, 1247–1256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.085
Ma, N., Tong, L., Li, Y., Yang, C., Tan, Q., & He, J. (2022). Distribution of antibiotics in lake water-groundwater - Sediment system in Chenhu Lake area. Environmental Research, 204, 112343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112343
Ma, Y., Li, M., Wu, M., Li, Z., & Liu, X. (2015). Occurrences and regional distributions of 20 antibiotics in water bodies during groundwater recharge. Science of The Total Environment, 518–519, 498–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.02.100
McRose, D. L., & Newman, D. K. (2021). Redox-active antibiotics enhance phosphorus bioavailability. Science, 371(6533), 1033–1037. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abd1515
Menció, A., & Mas-Pla, J. (2019). Assessing the Influence of Environmental Factors on Groundwater Antibiotic Occurrence by Means of Variation Partitioning. Water, 11(7), 1495. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071495
Mirzaei, R., Mesdaghinia, A., Hoseini, S. S., & Yunesian, M. (2019). Antibiotics in urban wastewater and rivers of Tehran, Iran: Consumption, mass load, occurrence, and ecological risk. Chemosphere, 221, 55–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.187
Montesdeoca-Esponda, S., Palacios-Díaz, M. del P., Estévez, E., Sosa-Ferrera, Z., Santana-Rodríguez, J. J., & Cabrera, M. del C. (2021). Occurrence of Pharmaceutical Compounds in Groundwater from the Gran Canaria Island (Spain). Water, 13(3), 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030262
Navarro, T. (2018). Water reuse and desalination in Spain – challenges and opportunities. Journal of Water Reuse and Desalination, 8(2), 153–168. https://doi.org/10.2166/wrd.2018.043
Nkoh, J. N., Shang, C., Okeke, E. S., Ejeromedoghene, O., Oderinde, O., Etafo, N. O., Mgbechidinma, C. L., Bakare, O. C., & Meugang, E. F. (2024). Antibiotics soil-solution chemistry: A review of environmental behavior and uptake and transformation by plants. Journal of Environmental Management, 354, 120312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.120312
Oliveira, T. S., Al Aukidy, M., & Verlicchi, P. (2017). Occurrence of Common Pollutants and Pharmaceuticals in Hospital Effluents (pp. 17–32). https://doi.org/10.1007/698_2017_9
Pan, M., & Chu, L. M. (2017). Fate of antibiotics in soil and their uptake by edible crops. Science of The Total Environment, 599–600, 500–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.214
Patyra, E., Nebot, C., Gavilán, R. E., Kwiatek, K., & Cepeda, A. (2023). Prevalence of veterinary antibiotics in natural and organic fertilizers from animal food production and assessment of their potential ecological risk. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 103(7), 3638–3644. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.12435
Pavelquesi, S. L. S., de Oliveira Ferreira, A. C. A., Rodrigues, A. R. M., de Souza Silva, C. M., Orsi, D. C., & da Silva, I. C. R. (2021). Presence of Tetracycline and Sulfonamide Resistance Genes in Salmonella spp.: Literature Review. Antibiotics, 10(11), 1314. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10111314
Picó, Y., Alvarez-Ruiz, R., Alfarhan, A. H., El-Sheikh, M. A., Alshahrani, H. O., & Barceló, D. (2020). Pharmaceuticals, pesticides, personal care products and microplastics contamination assessment of Al-Hassa irrigation network (Saudi Arabia) and its shallow lakes. Science of The Total Environment, 701, 135021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135021
Qiu, W., Hu, J., Magnuson, J. T., Greer, J., Yang, M., Chen, Q., Fang, M., Zheng, C., & Schlenk, D. (2020). Evidence linking exposure of fish primary macrophages to antibiotics activates the NF-kB pathway. Environment International, 138, 105624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105624
Rasschaert, G., Van Elst, D., Colson, L., Herman, L., de Carvalho Ferreira, H. C., Dewulf, J., Decrop, J., Meirlaen, J., Heyndrickx, M., & Daeseleire, E. (2020). Antibiotic Residues and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in Pig Slurry Used to Fertilize Agricultural Fields. Antibiotics, 9(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9010034
Ricart, S., & Rico, A. M. (2019). Assessing technical and social driving factors of water reuse in agriculture: A review on risks, regulation and the yuck factor. Agricultural Water Management, 217, 426–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2019.03.017
Robles-Jimenez, L. E., Aranda-Aguirre, E., Castelan-Ortega, O. A., Shettino-Bermudez, B. S., Ortiz-Salinas, R., Miranda, M., Li, X., Angeles-Hernandez, J. C., Vargas-Bello-Pérez, E., & Gonzalez-Ronquillo, M. (2021). Worldwide Traceability of Antibiotic Residues from Livestock in Wastewater and Soil: A Systematic Review. Animals, 12(1), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12010060
Rodríguez-Serin, H., Gamez-Jara, A., De La Cruz-Noriega, M., Rojas-Flores, S., Rodriguez-Yupanqui, M., Gallozzo Cardenas, M., & Cruz-Monzon, J. (2022). Literature Review: Evaluation of Drug Removal Techniques in Municipal and Hospital Wastewater. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(20), 13105. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013105
S. Al-Wasify, R., M. Alruwaili, M., S. Aljohani, F., R. Hamed, S., & Ragab, S. (2024). The Efficiency of Wastewater Treatment Plants for the Removal of Antibiotics. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.111999
Saki, M., Farajzadeh Sheikh, A., Seyed-Mohammadi, S., Asareh Zadegan Dezfuli, A., Shahin, M., Tabasi, M., Veisi, H., Keshavarzi, R., & Khani, P. (2022). Occurrence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from clinical specimens in southwest Iran: a multicentral study. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 2296. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-06128-4
Silori, R., & Tauseef, S. M. (2022). A Review of the Occurrence of Pharmaceutical Compounds as Emerging Contaminants in Treated Wastewater and Aquatic Environments. Current Pharmaceutical Analysis, 18(4), 345–379. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573412918666211119142030
Stigter, T. Y., Miller, J., Chen, J., & Re, V. (2023). Groundwater and climate change: threats and opportunities. Hydrogeology Journal, 31(1), 7–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-022-02554-w
Strawn, D. G. (2021). Sorption Mechanisms of Chemicals in Soils. Soil Systems, 5(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems5010013
Tal, A. (2016). Rethinking the sustainability of Israel’s irrigation practices in the Drylands. Water Research, 90, 387–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.12.016
Tasho, R. P., & Cho, J. Y. (2016). Veterinary antibiotics in animal waste, its distribution in soil and uptake by plants: A review. Science of The Total Environment, 563–564, 366–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.140
Taylor, P., & Reeder, R. (2020). Antibiotic use on crops in low and middle-income countries based on recommendations made by agricultural advisors. CABI Agriculture and Bioscience. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43170-020-00001-y
Tran, N. H., Reinhard, M., & Gin, K. Y.-H. (2018). Occurrence and fate of emerging contaminants in municipal wastewater treatment plants from different geographical regions-a review. Water Research, 133, 182–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.12.029
Van Boeckel, T. P., Brower, C., Gilbert, M., Grenfell, B. T., Levin, S. A., Robinson, T. P., Teillant, A., & Laxminarayan, R. (2015). Global trends in antimicrobial use in food animals. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112(18), 5649–5654. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1503141112
Viana, P., Meisel, L., Lopes, A., de Jesus, R., Sarmento, G., Duarte, S., Sepodes, B., Fernandes, A., dos Santos, M. M. C., Almeida, A., & Oliveira, M. C. (2021). Identification of Antibiotics in Surface-Groundwater. A Tool towards the Ecopharmacovigilance Approach: A Portuguese Case-Study. Antibiotics, 10(8), 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10080888
Vo, T.-K.-Q., Bui, X.-T., Chen, S.-S., Nguyen, P.-D., Cao, N.-D.-T., Vo, T.-D.-H., Nguyen, T.-T., & Nguyen, T.-B. (2019). Hospital wastewater treatment by sponge membrane bioreactor coupled with ozonation process. Chemosphere, 230, 377–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.009
Vymazal, J. (2018). Constructed Wetlands for Water Quality Regulation. In The Wetland Book (pp. 1313–1320). Springer Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-9659-3_234
Wu, W., Ma, M., Hu, Y., Yu, W., Liu, H., & Bao, Z. (2021). The fate and impacts of pharmaceuticals and personal care products and microbes in agricultural soils with long term irrigation with reclaimed water. Agricultural Water Management, 251, 106862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.106862
Xiao, W., Zhao, X., Teng, Y., Wu, J., & Zhang, T. (2023). Review on Biogeochemical Characteristics of Typical Antibiotics in Groundwater in China. Sustainability, 15(8), 6985. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086985
Xu, Y., Yu, X., Xu, B., Peng, D., & Guo, X. (2021). Sorption of pharmaceuticals and personal care products on soil and soil components: Influencing factors and mechanisms. Science of The Total Environment, 753, 141891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141891
Yao, L., Wang, Y., Tong, L., Deng, Y., Li, Y., Gan, Y., Guo, W., Dong, C., Duan, Y., & Zhao, K. (2017). Occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in surface water and groundwater from different depths of aquifers: A case study at Jianghan Plain, central China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 135, 236–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.10.006
Yuan, W., Tian, T., Yang, Q., & Riaz, L. (2020). Transfer potentials of antibiotic resistance genes in Escherichia spp. strains from different sources. Chemosphere, 246, 125736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125736
Yuan, X., Hu, J., Li, S., & Yu, M. (2020). Occurrence, fate, and mass balance of selected pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) in an urbanized river. Environmental Pollution, 266, 115340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115340
Zhang, H., Bai, J., Xue, W., Xue, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Quantum chemical prediction of effects of temperature on hydrolysis rate of penicillin under weakly acidic condition. Science of The Total Environment, 806, 150509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150509
Zhi, D., Yang, D., Zheng, Y., Yang, Y., He, Y., Luo, L., & Zhou, Y. (2019). Current progress in the adsorption, transport and biodegradation of antibiotics in soil. Journal of Environmental Management, 251, 109598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109598
Zhou, X., Wang, J., Lu, C., Liao, Q., Gudda, F. O., & Ling, W. (2020). Antibiotics in animal manure and manure-based fertilizers: Occurrence and ecological risk assessment. Chemosphere, 255, 127006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127006
Zhuang, S., & Wang, J. (2023). Interaction between antibiotics and microplastics: Recent advances and perspective. Science of The Total Environment, 897, 165414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.165414
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Sahury Jellitza Quispe-Durand, Franz Zirena-Vilca

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Los autores que publican en esta revista aceptan los siguientes términos:
- Los autores conservan los derechos de autor y conceden a la revista el derecho publicación con la obra, simultáneamente licenciada bajo una licencia de Creative Commons CC By que permite a otros compartir el trabajo, pero citando la publicación inicial en esta revista.
- Los autores pueden celebrar acuerdos contractuales adicionales separados para la distribución no exclusiva de la versión publicada de la obra de la revista (por ejemplo, publicarla en un repositorio institucional o publicarla en un libro), pero citando la publicación inicial en esta revista.
- Se permite y anima a los autores a publicar su trabajo en línea (por ejemplo, en repositorios institucionales o en su sitio web) antes y durante el proceso de presentación, ya que puede conducir a intercambios productivos, así como una mayor citación del trabajo publicado (https://web-archive.southampton.ac.uk/opcit.eprints.org/oacitation-biblio.html)














