Assessment of noise pollution in northeastern Peru
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55996/dekamuagropec.v6i2.372Keywords:
Noise pollution; noise measurement; sound pressureAbstract
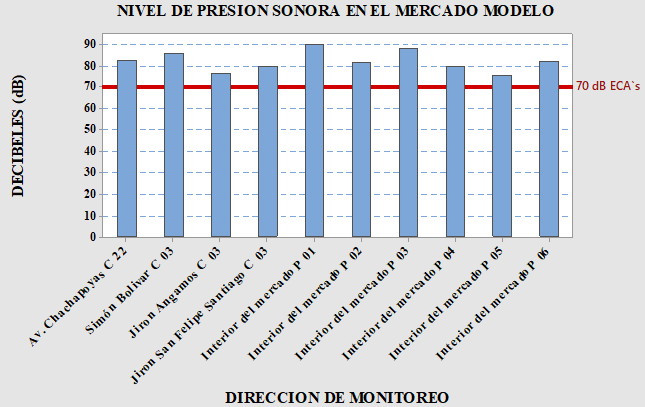
The district of Bagua Grande, province of Utcubamba, Amazonas region, faces a severe noise pollution problem due to its rapid population growth and the consequent increase in vehicular traffic. Factors such as excessive use of horns, the age of the vehicle fleet, and the lack of mufflers intensify the noise, impacting quality of life. The main objective of this research was to evaluate noise pollution in the district and compare sound pressure levels (SPL) with Supreme Decree No. 085-2003-PCM. The methodology used followed the National Protocol for Environmental Noise Monitoring (Supreme Decree No. 227-2013-MINAM). Monitoring was carried out between October and December 2020, during daytime hours (6:00 a.m. to 8:00 a.m. and 12:00 p.m. to 2:00 p.m.). Sixty points (40 urban and 20 commercial) were measured at a height of 1.5 m, totaling 180 measurements. The results concluded that there was widespread non-compliance with the National Environmental Quality Standard (ECA) of 60 dB. In the urban area, the La Esperanza sector was the most affected, with 9 out of 10 points exceeding the permitted limit, followed by San Martín (7 out of 10 points). The most critical situation was recorded in commercial areas, particularly the Mercado Modelo market, where 100% of the points sampled exceeded 70 dB, with peaks of up to 95.4 dB at the Parada Municipal market. It is concluded that Bagua Grande has noise levels that pose a significant risk to public health and require urgent regulatory and enforcement action.
Downloads
References
Andrade, R., & Mas, M. (2024). La contaminación sonora y su impacto en el Perú. https://www.pucp.edu.pe/climadecambios/noticias/la-contaminacion-sonora-y-su-impacto-en-el-peru/
Chaux Alvarez, L. M., & Acevedo Buitrago, B. (2019). Evaluación de ruido ambiental en alrededores a centros médicos de la localidad Barrios Unidos, Bogotá. Revista Científica, 2(35), 234–246. https://doi.org/10.14483/23448350.13983
Chávez Collantes, A., Velarde Apaza, L. D., Gonzáles García, J. E., Chávez Collantes, A., Castillo Rojas, E. W., Díaz Estrada, J. A., & Seminario Cunya, A. (2023). Riesgo ambiental por contaminación sonora ocasionado por el parque automotor en la ciudad de Celendín, Perú. Revista Ciencia Nor@ndina, 6(2), 205–221. https://doi.org/10.37518/2663-6360X2023v6n2p205
Mendoza, É. C., Legua Laurencio, J. L., & Condori Apaza, R. M. (2018). Determination of the sound pressure level generated by the vehicle fleet in the city of Ilo, Peru. Produccion y Limpia, 13(2), 14–20. https://doi.org/10.22507/pml.v13n2a2
MINAN. (2003). Estándares Nacionales de Calidad Ambiental para Ruido. https://sinia.minam.gob.pe/normas/reglamento-estandares-nacionales-calidad-ambiental-ruido
MINAN. (2014). Protocolo nacional de monitoreo de ruido ambiental.
Ocas Tasilla, A. (2018). La Contaminación Acústica del Sector Transporte y sus Consecuencias en la Salud de la Población del Distrito de Cajamarca 2011-2015. Repositorio Institucional - UNC, 158. https://repositorio.unc.edu.pe/handle/20.500.14074/1890
Quispe, J. C., Roque, C. E., Rivera, G. F., Rivera, F. A., & Romani, A. (2021). Impacto de la contaminación sonora en la salud de la población de la ciudad de Juliaca, Perú. Ciencia Latina Revista Científica Multidisciplinar, 5(1), 311–337.
Reyes Jimenez, H. A. (2011). Estudio y plan de mitigación del nivel de ruido ambiental en la zona urbana de la ciudad de puyo. https://1library.co/document/qvl9l71y-estudio-plan-mitigacion-nivel-ruido-ambiental-urbana-ciudad.html
Rivera Da Costa, A. S. M. (2014). Estudio de los niveles de ruido y los ECAS para para ruido, en los principales centros de salud, en la ciudad de Iquitos. 53. http://dspace.unapiquitos.edu.pe/bitstream/unapiquitos/258/1/TESIS PARA LIBRO ANGIE RIVERA DACOSTA - MAYO 2014.pdf
Sequeira, M. E., & Cortínez, V. H. (2011). Diseño acústico óptimo de la geometria de salas de concierto. XXX, 3259–3269.
Solís Fonseca, J. P., Salazar Bravo, L. C., Romero Carrión, V. L., & Solís Salazar, A. D. L. Á. C. (2022). Congestión Vehicular y Contaminación Ambiental en Lima Metropolitana. Revista Lasallista de Investigación, 19(1), 152–164. https://doi.org/10.22507/rli.v19n1a9
Zamorano González, B., Peña Cárdenas, F., Parra Sierra, V., Velázquez Narváez, Y., & Vargas Martínez, J. I. (2015). Noise pollution in Matamoros downtown. Acta Universitaria, 25(5), 20–27. https://doi.org/10.15174/au.2015.819
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Irael Ruiz-Tafur, Anthonny Smith Guevara-Flores

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Los autores que publican en esta revista aceptan los siguientes términos:
- Los autores conservan los derechos de autor y conceden a la revista el derecho publicación con la obra, simultáneamente licenciada bajo una licencia de Creative Commons CC By que permite a otros compartir el trabajo, pero citando la publicación inicial en esta revista.
- Los autores pueden celebrar acuerdos contractuales adicionales separados para la distribución no exclusiva de la versión publicada de la obra de la revista (por ejemplo, publicarla en un repositorio institucional o publicarla en un libro), pero citando la publicación inicial en esta revista.
- Se permite y anima a los autores a publicar su trabajo en línea (por ejemplo, en repositorios institucionales o en su sitio web) antes y durante el proceso de presentación, ya que puede conducir a intercambios productivos, así como una mayor citación del trabajo publicado (https://web-archive.southampton.ac.uk/opcit.eprints.org/oacitation-biblio.html)














