Desarrollo y validaci n de
m todo cromatogr fico para la detecci n y cuantificaci n de residuos de
Ivermectina en agua residual
Development and validation
of a chromatographic method for the detection and quantification of Ivermectin
residues in wastewater
Desenvolvimento e
valida o de um m todo cromatogr fico para a dete o e quantifica o de
res duos de Ivermectina em guas residuais
Elvis
Jack Colque-Ayma,2 *, Donald Efrain Merma-Chacca,
*, Donald Efrain Merma-Chacca, Alejandro Manuel Ecos-Espino1,
Alejandro Manuel Ecos-Espino1, Clara Nely
Campos-Quir z2,3
Clara Nely
Campos-Quir z2,3 Jos Luis
Ramos-Tejada1,2
Jos Luis
Ramos-Tejada1,2 Anyela Pierina
Veja-Quispe1
Anyela Pierina
Veja-Quispe1 , Franz Zirena-Vilca1,2
, Franz Zirena-Vilca1,2
DOI: https://doi.org/10.55996/dekamuagropec.v4i2.192
RESUMEN
Este estudio
desarroll y valid un m todo de an lisis por UHPL-DAD para detectar y
cuantificar residuos de Ivermectina (IVM) en agua residual. La implementaci n
de este m todo, consisti en poder realizar un m todo robusto y eficiente; donde
el tiempo de retenci n para este residuo en menci n fue de 3.1 min. No
obstante, los par metros considerados en el proceso de validaci n del m todo
anal tico fueron: selectividad, linealidad, l mite de detecci n, l mite de
cuantificaci n y porcentaje de recuperaci n; el m todo es selectivo, el
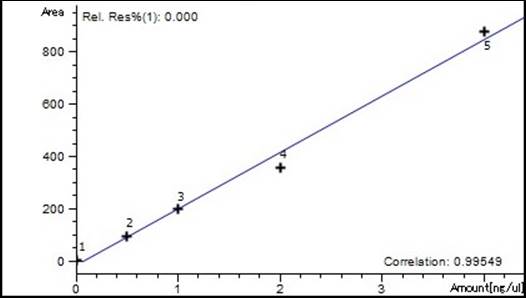
coeficiente de correlaci n es R2 ≥ 0,99, presenta un l mite de
detecci n (LD) de 0,003 g L-1, un l mite de cuantificaci n (LQ) de
0,01 g L-1, y un porcentaje de recuperaci n del 90% (con
fortificaci n de 0,1 g L-1).
Palabras
claves: Validaci n,
Antiparasitario, Ivermectina, Cromat grafo, Cuantificaci n.
ABSTRACT
This study developed and
validated a method of analysis by UHPL-DAD to detect and quantify Ivermectin (IVM)
residues in wastewater. The implementation of this method consisted of a robust
and efficient method, where the retention time for this residue was 3.1 min.
However, the parameters considered in the validation process of the analytical
method were: selectivity, linearity, detection limit, quantification limit and
recovery percentage; the method is selective, the correlation coefficient is R2
≥ 0.99, it presents a detection limit (LD) of 0.003 g L-1, a
quantification limit (LQ) of 0.01 g L-1, and a recovery percentage
of 90% (with fortification of 0.1 g L-1).
Keywords: Validation, Antiparasitic, Ivermectin, Chromatograph,
Quantification.
RESUMO
Este estudo desenvolveu e
validou um m todo de an lise por UHPL-DAD para detectar e quantificar res duos
de Ivermectina (IVM) em guas residuais. A implementa o deste m todo consistiu
num m todo robusto e eficiente, onde o tempo de reten o para este res duo foi
de 3,1 min. No entanto, os par metros considerados no processo de valida o do
m todo anal tico foram: seletividade, linearidade, limite de dete o, limite de
quantifica o e percentagem de recupera o; o m todo seletivo, o coeficiente
de correla o R2 ≥ 0,99, apresenta um limite de dete o (LD) de 0,003
g L-1, um limite de quantifica o (LQ) de 0,01 g L-1, e
uma percentagem de recupera o de 90% (com fortifica o de 0,1 g L-1).
Palavras-chave: Valida o, Antiparasit rio, Ivermectina, Cromat grafo,
Quantifica
Ammon, A. (2020).
Contributing to health security in Europe since 2005 ECDC s 15th anniversary.
Eurosurveillance, 25(20), 1 4.
https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.20.2000975
Anal ticos,
M. (2020). Instituto Nacional de Metrologia, Qualidade e T cnologia.
Orienta o sobre valida o de m todos anal ticos - DOQ-CGCRE-008. Brasil.
http://www.inmetro.gov.br/Sidoq/pesquisa_link.asp?seq_tipo_documento=5&cod_uo_numeracao=00774&num_documento=008
Chedid,
M., Waked, R., Haddad, E., Chetata, N., Saliba, G., & Choucair, J. (2021).
Antibiotics in treatment of COVID-19 complications: a review of frequency,
indications, and efficacy. Journal of Infection and Public Health, 14(5),
570 576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiph.2021.02.001
Cristina,
I., & Fontes, S. (2010). Extra o em Fase S lida : Fundamentos
Te ricos e Novas Estrat gias para Prepara o de Fases S lidas. 2, 13 25.
Elsaid,
K., Olabi, V., Sayed, E. T., Wilberforce, T., & Abdelkareem, M. A. (2021).
Effects of COVID-19 on the environment: An overview on air, water, wastewater,
and solid waste. Journal of Environmental Management, 292(April),
112694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112694
Fatoki,
O. S., Opeolu, B. O., Genthe, B., & Olatunji, O. S. (2018). Multi-residue
method for the determination of selected veterinary pharmaceutical residues in
surface water around Livestock Agricultural farms. Heliyon, 4(12), e01066.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e01066
Gras,
M., Champel, V., Masmoudi, K., & Liabeuf, S. (2020). Self-medication practices
and their characteristics among French university students. Therapie.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.therap.2020.02.019
Hiller,
C. X., H bner, U., Fajnorova, S., Schwartz, T., & Drewes, J. E. (2019).
Antibiotic microbial resistance (AMR) removal efficiencies by conventional and
advanced wastewater treatment processes: A review. Science of the Total
Environment, 685, 596 608.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.315
Koch,
D. E., Bhandari, A., Close, L., & Hunter, R. P. (2005). Azithromycin
extraction from municipal wastewater and quantitation using liquid
chromatography/mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1074(1 2),
17 22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2005.03.052
Monteiro,
S. H., Francisco, J. G., Campion, T. F., Pimpinato, R. F., Moura Andrade, G. C.
R., Garcia, F., & Tornisielo, V. L. (2015). Multiresidue antimicrobial
determination in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis Niloticus) cage farming by liquid
chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Aquaculture, 447, 37 43.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.07.002
Nieto-Ju rez,
J. I., Torres-Palma, R. A., Botero-Coy, A. M., & Hern ndez, F. (2021). Pharmaceuticals and
environmental risk assessment in municipal wastewater treatment plants and
rivers from Peru. Environment International, 155(March).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2021.106674
Padivitage,
N., Adhikari, S., & Rustum, A. M. (2022). Simultaneous determination of
ivermectin, clorsulon and their related substances in an injectable finished
product by a stability-indicating RP-HPLC method. Journal of Pharmaceutical
and Biomedical Analysis, 210, 114580.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2022.114580
Pawar,
R. P., Durgbanshi, A., Bose, D., Peris-Vicente, J., Albiol-Chiva, J.,
Esteve-Romero, J., & Carda-Broch, S. (2021). Determination of albendazole and
ivermectin residues in cattle and poultry-derived samples from India by
micellar liquid chromatography. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,
103(March), 104111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2021.104111
Pazda,
M., Kumirska, J., Stepnowski, P., & Mulkiewicz, E. (2019). Antibiotic
resistance genes identified in wastewater treatment plant systems A review. Science
of the Total Environment, 697, 134023.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134023
Rawson,
T. M., Ming, D., Ahmad, R., Moore, L. S. P., & Holmes, A. H. (2020).
Antimicrobial use, drug-resistant infections and COVID-19. Nature Reviews
Microbiology, 18(8), 409 410.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-020-0395-y
Ribani,
M., Grespan Bottoli, C. B., Collins, C. H., Fontes Jardim, I. C. S., &
Costa Melo, L. F. (2004). Valida o em m todos cromatogr ficos e
eletrofor ticos. Quimica Nova, 27(5), 771 780.
https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422004000500017
Xu, J.,
Xu, Y., Wang, H., Guo, C., Qiu, H., He, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2014). Chemosphere Occurrence of
antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in a sewage treatment plant and its
effluent-receiving river. CHEMOSPHERE. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.02.040
![]() *, Donald Efrain Merma-Chacca1,[2]
*, Donald Efrain Merma-Chacca1,[2]![]() Alejandro Manuel Ecos-Espino1,[3]
Alejandro Manuel Ecos-Espino1,[3]![]() Clara Nely
Campos-Quir z2,3
Clara Nely
Campos-Quir z2,3![]() Jos Luis
Ramos-Tejada1,2
Jos Luis
Ramos-Tejada1,2![]() Anyela Pierina
Veja-Quispe1
Anyela Pierina
Veja-Quispe1![]() , Franz Zirena-Vilca1,2
, Franz Zirena-Vilca1,2![]()